What is immersion education?
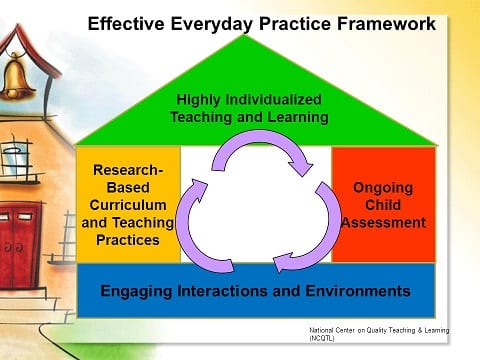
Immersion education is a teaching method where students learn all subjects in a target language like French, Spanish, or Mandarin. It works best when children start early, as they can easily pick up language nuances. These classrooms offer efficient learning environments with quick transitions.
Teachers who are fluent and native speakers of the target language, commit to speaking it consistently. They use the target language during instruction, transitions, outdoor play, and meal times. Teachers pay close attention to students’ needs and individual learning styles.
The classroom features a literacy-rich environment with pictures, labels, and meaningful visuals to support the target language throughout the day. Teachers adeptly help comprehension through non-verbal clues and smart teaching strategies.
Days are organized, routines are consistent, and key phrases and vocabulary repeat often to boost vocabulary development. Children make connections across the curriculum as the target language and English curriculum align, reinforcing concepts and ideas in both languages.
Will your child lose their English?
Research indicates that children in immersion settings perform the same or better than their non-immersion peers.
What if you don’t speak the target language at home?
Your child can still succeed and gain proficiency even if you don’t speak the target language. Homework uses songs and games to review classroom learning in a fun and engaging way. Strong communication with your child’s teacher is essential for success.